
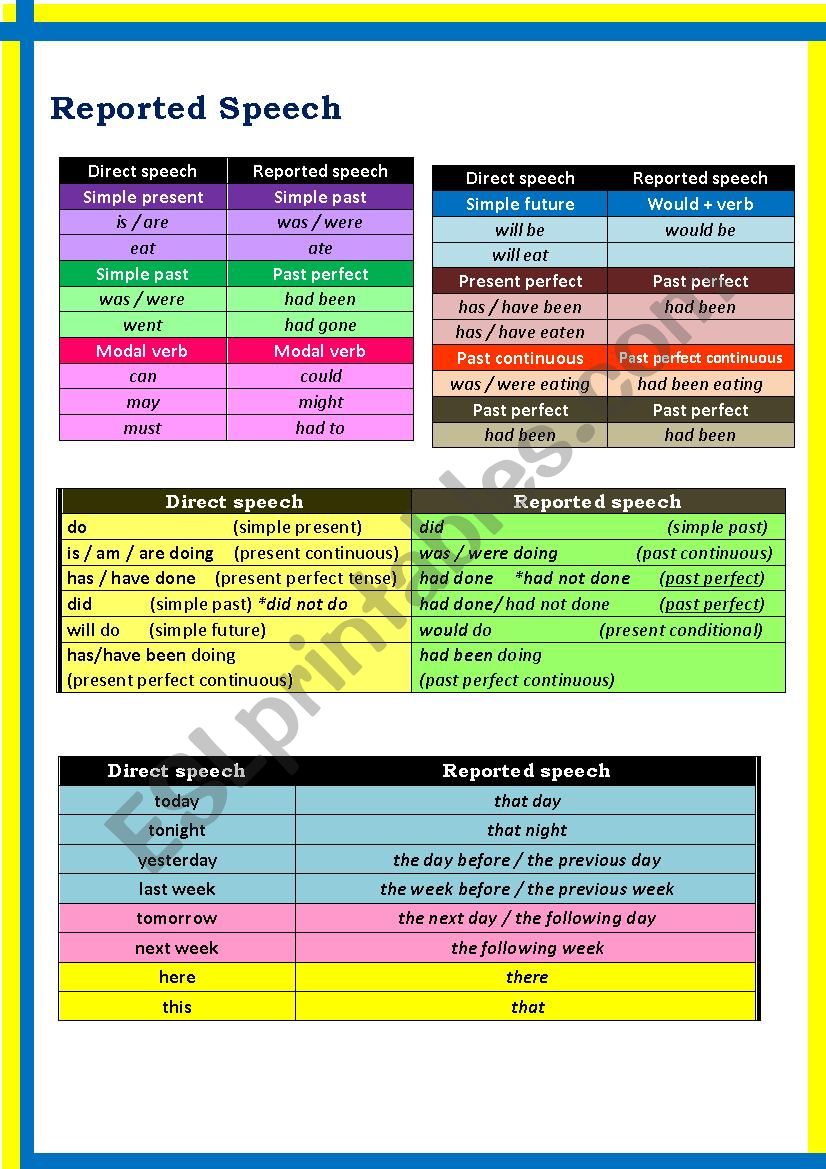
He said that he would buy Mercedes if he had been rich" 3. Examples of the main changes in verb tense He said, “I am happy.” – He said that he was happy.

You must change the tense if the introductory clause (i.e., the reporting verb) is in the past tense (e. g. He says, “I write poems.” – He says that he writes English. Note, however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person singular). (backshift) "I write poems "ĭo not change the tense if the introductory clause (i.e., the reporting verb) is in the present tense (e. g. Shifting back tense Direct speech Reported speech (no backshift) “I write poems.” He says that he writes poems.

When transforming statements, check whether you have to change: When you use reported speech, you either report: He asked Betty: "Do you like cheese?" He wanted to know if Betty liked cheese. She said: "I'm visiting Paris next weekend." She said that she was visiting Paris the following weekend. More examples: Direct speech Reported speech She says: "I like tuna fish." She says that she likes tuna fish.
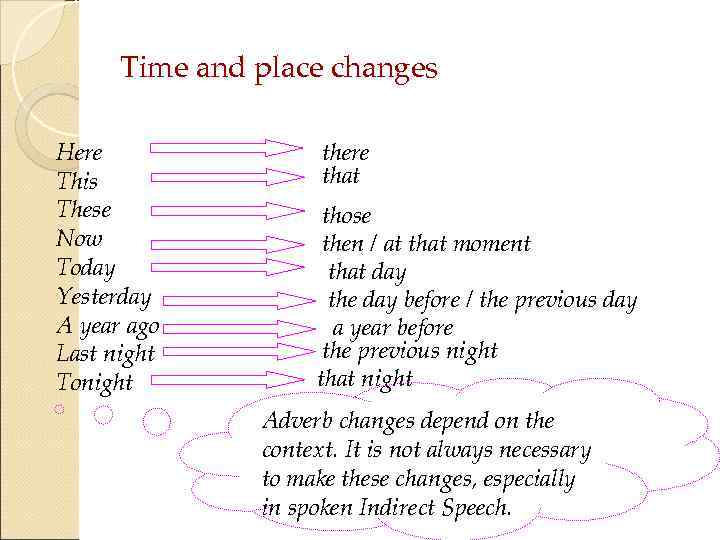
Some changes are necessary: the time expressions, the tense of the verbs, and the demonstratives. We do not necessarily report the speaker's exact words. Reported speech is a way of reporting what someone said without using quotation marks.
We add a reporting verb such as "he said" or "she asked" before or after the quote.Ģ. We put their words within quotation marks. We use direct speech to quote a speaker's exact words. Reported speech is also referred to as indirect speech or indirect discourse.īefore explaining how to report a discourse, let us first distinguish between direct speech and reported speech.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
